Introduction
Cooling towers are essential components of industrial and commercial facilities that play a crucial role in maintaining optimal operating conditions for various processes. These towering structures are designed to dissipate excess heat کولینگ تاور by machinery, manufacturing processes, or HVAC systems. In this article, we will explore the functions, types, and importance of cooling towers in diverse industries.
The Basics of Cooling Towers
Cooling towers are heat rejection devices that transfer excess heat to the atmosphere through the evaporation of water. Their primary purpose is to remove heat from a system by allowing a small stream of water to evaporate, thereby cooling the remaining water. This process ensures that industrial processes or equipment can operate efficiently without the risk of overheating.
How Cooling Towers Work
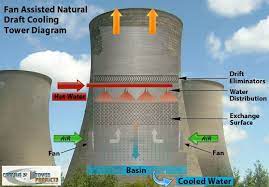
Cooling towers operate on the principle of evaporative cooling. Hot water from industrial processes or HVAC systems is pumped into the tower, where it cascades down a series of fill media. The fill media enhances the contact between the water and air, promoting evaporation. As the water evaporates, it absorbs heat from the remaining water, lowering its temperature.
Simultaneously, a fan or a natural draft induces air through the tower, further facilitating the evaporation process. The cooled water is then recirculated back into the industrial process or system, ready to absorb more heat. This cyclic process ensures that the equipment or processes receiving the cooled water can maintain optimal operating temperatures.
Types of Cooling Towers
Cooling towers come in various designs and configurations to suit different industrial needs. The two main types are:
- Natural Draft Cooling Towers:
- These towers rely on the natural buoyancy of air to move it through the tower.
- Typically larger in size and used for heavy-duty industrial applications.
- Well-suited for power plants and large manufacturing facilities.
- Mechanical Draft Cooling Towers:
- Equipped with fans that actively draw or force air through the tower.
- More compact and versatile, making them suitable for a range of applications, including HVAC systems and smaller industrial processes.
Applications in Different Industries
Cooling towers find applications in a wide array of industries, including:
- Power Plants:
- Crucial for cooling the condenser water in power plants, ensuring efficient electricity generation.
- Manufacturing:
- Used in various manufacturing processes, such as metal production and chemical manufacturing, to control temperatures and maintain product quality.
- HVAC Systems:
- Integral in air conditioning systems, cooling towers help regulate building temperatures and provide comfort for occupants.
- Oil Refineries:
- Essential for cooling various stages of the refining process, preventing equipment damage and ensuring optimal operation.
Benefits of Cooling Towers
The use of cooling towers offers several advantages:
- Energy Efficiency:
- Evaporative cooling is an energy-efficient method of heat dissipation, reducing the overall energy consumption of industrial processes.
- Environmental Sustainability:
- By using the ambient air for cooling, cooling towers minimize the environmental impact compared to alternative methods that rely on large amounts of water.
- Cost-Effectiveness:
- Cooling towers provide a cost-effective solution for managing heat in industrial processes, contributing to overall operational efficiency.
Conclusion
Cooling towers are indispensable components in modern industries, contributing to the efficiency and sustainability of various processes. As technology continues to advance, the design and implementation of cooling towers will evolve, ensuring their continued role in maintaining optimal operating conditions for diverse applications across industries.